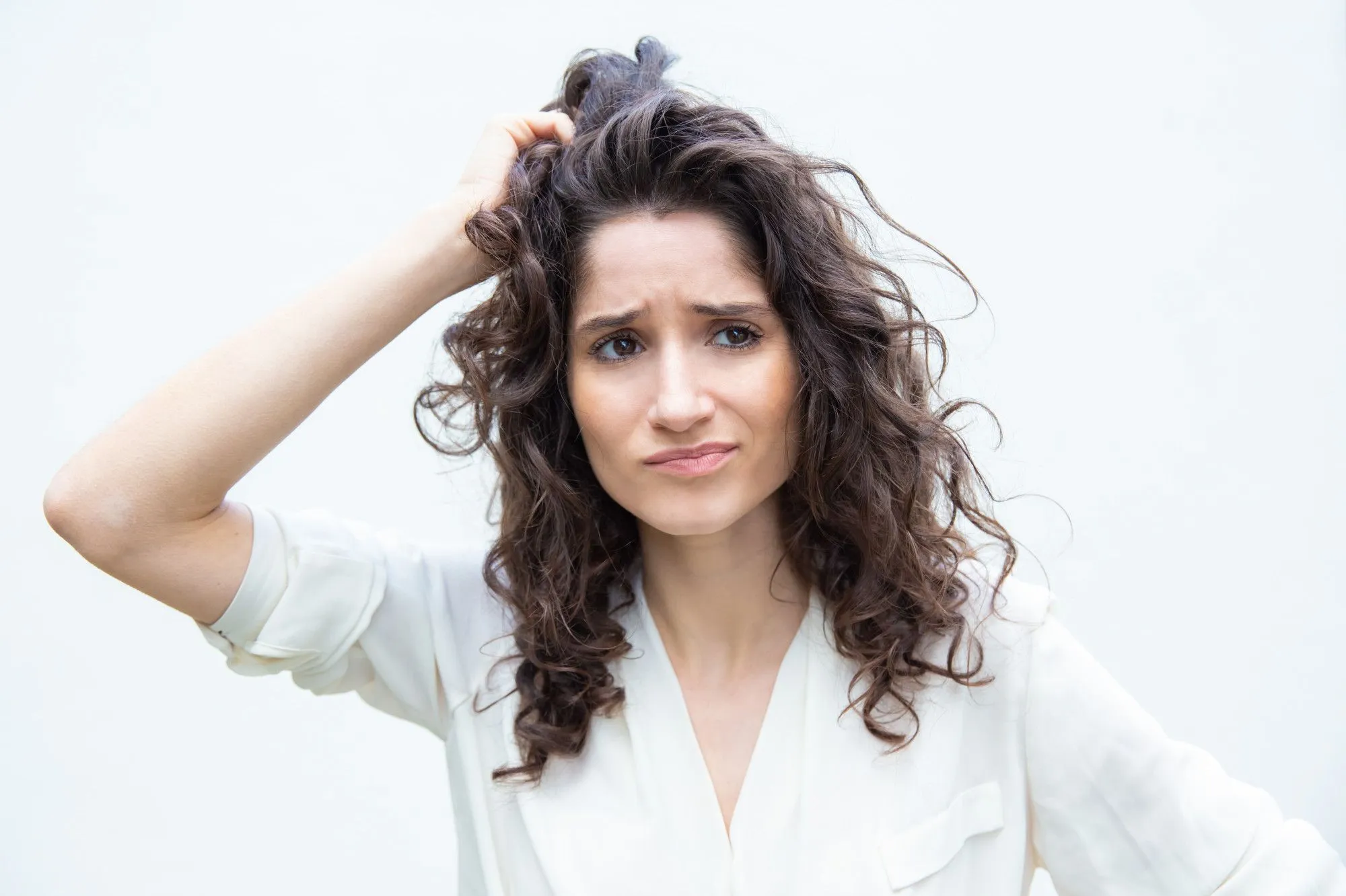
Female hair loss, a concern impacting many women, arises from various factors and can significantly affect confidence and self-image. While men are typically more open in seeking solutions for hair loss, women often face feelings of isolation and depression as they tend to keep their struggles private.
However, hair loss is prevalent among females, affecting over 50% of women at some point in their lives and approximately 80% by age 80. The primary culprit behind female hair loss is female pattern hair loss, scientifically termed androgenetic alopecia, which affects about 30 million women in the United States.
Schedule a appointment today with Dermatologist in Northridge.
Understanding the causes and seeking effective remedies for female hair loss is paramount in restoring confidence and self-assurance.
How Does Female Hair Loss Differ from Male Hair Loss
involve androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as pattern baldness, the presentation and progression of hair loss vary between genders.
In men, hair loss typically follows a well-defined pattern characterized by a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, resulting in a distinct “M” shape. Over time, this may progress to partial or complete baldness.
On the other hand, female hair loss tends to manifest as overall thinning rather than distinct patterns. Women generally do not experience significant hairline recession, and complete baldness is less common. Instead, the hair becomes thinner throughout the scalp, often retaining the natural hairline.
Understanding these differences is crucial in diagnosing and addressing hair loss effectively in both men and women.
Why Am I Losing My Hair?
Hair loss can be attributed to various factors, both internal and external. Common reasons for hair loss include:
Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in determining whether you are prone to hair loss. If your parents or close relatives experienced hair loss, you may be more likely to experience it too.
Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as those experienced during pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or thyroid disorders, can contribute to hair loss.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions like alopecia areata, autoimmune diseases, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and thyroid disorders can lead to hair loss.
Medications: Some medications, including those used for cancer, arthritis, depression, heart problems, and high blood pressure, can cause hair loss as a side effect.
Stress: Emotional or physical stress can trigger a type of hair loss called telogen effluvium, where hair follicles prematurely enter the resting phase and shed more than usual.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate intake of essential nutrients like iron, protein, vitamins (especially biotin), and minerals can lead to hair loss.
Hairstyling Habits: Excessive heat styling, tight hairstyles (like ponytails or braids), and chemical treatments can damage the hair and contribute to hair loss.
Hair naturally becomes thinner and more prone to breakage as we age, leading to gradual hair loss over time.
If you’re experiencing significant hair loss or are concerned about it, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and explore appropriate treatment options.
How Can I Treat Female Hair Loss?
Treatment for female hair loss varies depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here are some common approaches:
Medications:
- Minoxidil: An over-the-counter topical treatment applied to the scalp, which can help stimulate hair growth.
- Finasteride: A prescription medication that blocks the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which can contribute to hair loss.
Hormone Therapy:
Hormonal imbalances, such as those associated with menopause or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), may be treated with hormone replacement therapy or other hormonal medications.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
This procedure involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood into the scalp to promote hair growth.
Hair Transplant Surgery:
In cases of significant hair loss, hair transplant surgery may be an option. This involves transplanting hair follicles from one part of the scalp to areas of thinning or baldness.
Scalp Treatments:
Certain shampoos, conditioners, and scalp treatments containing ingredients like ketoconazole or minoxidil may help improve scalp health and promote hair growth.
Lifestyle Changes:
- Maintaining a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals essential for hair health.
- Avoiding tight hairstyles and harsh hair treatments that can damage the hair follicles.
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques or therapy, as stress can exacerbate hair loss.
It’s important to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual needs and preferences. Additionally, addressing any underlying medical conditions contributing to hair loss is essential for effective management.